Note:
This documentation is currently being reworked, but still available here if needed.
Thinking in Norce Checkout
This page will be a good starting page to get a feel for how the Norce Checkout works, and how each part of the checkout process is connected and works together.
The Norce Checkout System
There are four main parts of the Norce Checkout system:
- Adapters
- Configuration
- Frontend
- Order
Adapters
Adapters are the connectors to the different payment providers and other services that are needed to complete the checkout process. Manipulating the order in anyway from the frontend is done by communicating with an adapter. The adapter is then responsible for updating the order and making sure any external system is synchronized with the Norce order.
Configuration
What?
Handle storage of arbitrary, but strongly typed, JSON in the configuration API. A configuration is a JSON object that is bound to a merchant, channel and a configuration id.
Requirements:
-
Include a
$schemafield to describe your data. -
Have a unique identifier (
id).
Optional (mostly for adapters):
-
Declare
adapter.internalUrlandadapter.publicUrl, which are used in the system as base urls when communicating with the adapter. -
active: boolean, indicating whether or not the adapter is active. If having multiple primary payments for instance, only one should be active.
How?
Adapters create a JSON schema for their configuration data and make it publicly available.
When a configuration is saved with a $schema field, the configuration service retrieves the schema associated with the json - and declared in the $schema field. This allows the configuration service to strongly validate the data, while also having no internal knowledge about the shape of the data, since its declared in the schema hosted by the adapter.
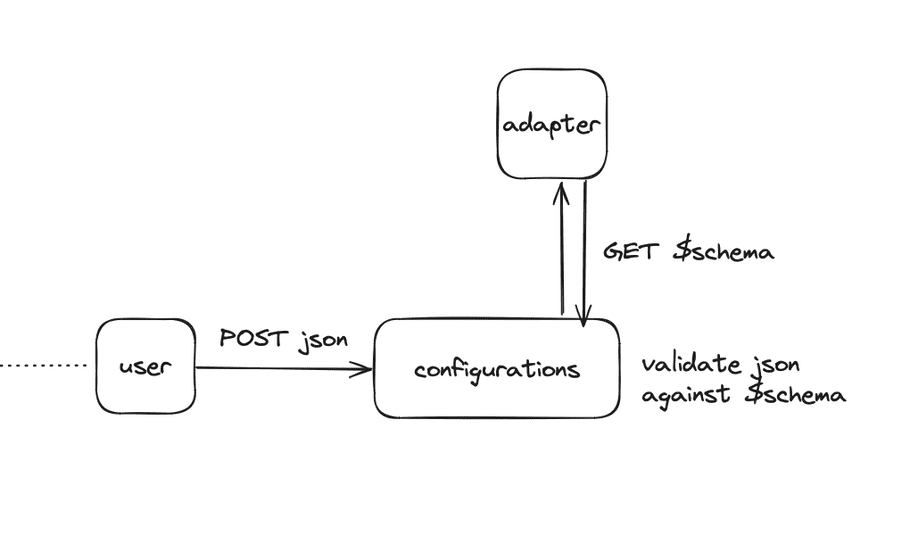
Why?
To store settings and configurations applicable to facilitate communication between Norce checkout and external systems (e.g., Klarna) without dependency on or knowledge of other adapters or components. This ensures compatibility and independence of individual parts of the system.
Frontend
The frontend is the part of the checkout a user can interact with. It should fetch and display the order. Any action the user can take, or events that might occur, should correspond to a request to an adapter.
Order
The order is the main object that is being processed through the checkout system and functions as the state of the checkout process. You can view the structure of an order here.
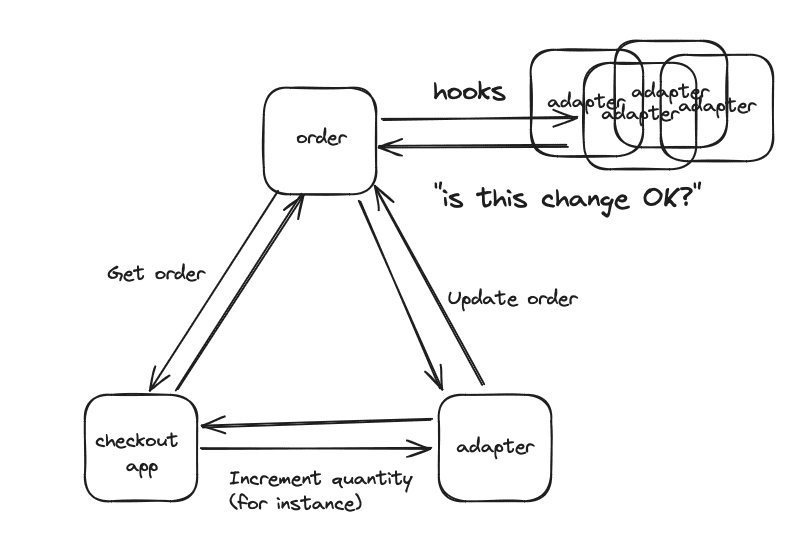
Hooks
Hooks are added to an order by adapters, and are a way handle side-effects of an order modification. For example this could be a cart update, updating the item quantity could affect shipping cost, which in turn could affect the payment total. An adapter can subscribe to changes in a particular place on the order, such that if a modification is made, it will have a say whether or not the modification is allowed, and if any other changes need to be made.
The example above you would have a shipping adapter interested in changes to the cart, and a payment adapter interested in changes to the cart and shipping.
A simplified way of looking at it can be seen in this image:
A more detailed view can be seen in this sequence diagram: